Define Unemployment and Explain Its Different Types
In practice these cannot be measured directly and they can often overlap but they provide a useful way of thinking about unemployment. There is a lot of confusion and disagreement regarding the meaning and nature of unemployment.

Unemployment Meaning And Types Economics Lessons Teaching Economics General Knowledge Facts
Figure 209 The Natural Level of Employment applies the demand and supply model to the labor market.

. When an individual is unemployed because they are looking for a new job. In strictly economic terms the unemployed include all those who are able and willing to work but cannot find work. This could occur when people are.
Each source of unemployment has quite different implications not only for the workers it affects but also for public policy. The period when worker search for job or switching a job from another job this is called frictional. As per the frictional unemployment definition this type of unemployment occurs due to the.
See the answer See the answer done loading. For example if you are an experienced professional in automotive manufacturing the rise of automation could mean that your skills become obsolete. These three types of unemployment are not independent of each other.
Three Types of Unemployment. Seasonal unemployment disguised unemployment and chronic unemployment. It occurs when changing demand patterns in an economy dislocate.
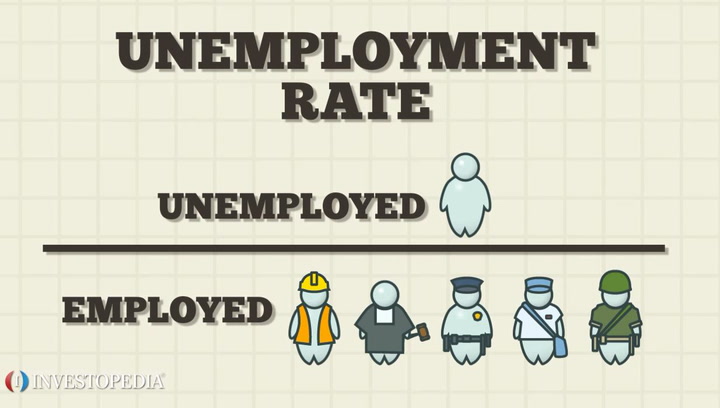
Unemployment is measured by the unemployment rate which is the number of people who are. Types of Unemployment 1. Learn about our Financial Review Board.
The types of unemployment are discussed below. These are- frictional unemployment structural unemployment and cyclical unemployment. Link unemployment to economic cycle for instance connect the types of unemployment to the points of the economic.
12 Different Types of Unemployment. Definition and Calculation Unemployment is a regularly used term and normally refers to those who are out of work. The second twostructural and frictionalmake up the natural unemployment rate.
For example a period of high cyclical unemployment might lift structural unemployment. Figure 55 The Natural Level of Employment applies the demand and supply model to the labor market. Broadly unemployment in India can be classified into two groups.
The price of labor is taken as the real wage which is the. Definition and Formula 834. As per the structural unemployment definition the market economies always have some kind of.
Definition Examples and Causes of Unemployment - 2022 - MasterClass. So to comprehend the problem in a proper way and suggest remedies we may discuss the various types of unemployment. Demand deficit unemployment is the biggest cause of unemployment that typically.
An example is a worker who recently quit or was fired and is looking for a job in an economy. Workers may find themselves unemployed for different reasons. Structural unemployment occurs when there is a disconnect between the skills you have and the skills needed by employers.
1 Cyclical unemployment is unfortunately the most familiar. Unemployment according to the OECD Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development is people above a specified age usually 15 not being in paid employment or self-employment but currently available for work during the reference period. Define economic cycle and explain its respective four points points of the economic cycle Define unemployment and explain the different types of unemployment.
Types of Unemployment Frictional Unemployment. Industrial unemployment and educated unemployment. Cyclical unemployment occurs with changes in economic activity over the business cycle.
Cyclical structural and frictional. The price of labor is taken as the real wage which is the. This unemployment arises when there is a mismatch between the workers skills and.
There are three main types of unemployment. Frictional unemployment occurs when people voluntarily change jobs within an economy. If unemployment continues to be a long term feature of a country it is called chronic unemployment.
Unemployment has three main types. Cyclical Frictional Structural 615 Natural Rate of Unemployment. It occurs during a recession.
Cyclical unemployment is the variation in the number of unemployed workers over the course of. Types of Unemployment. The following points highlight the five main types of unemployment that occurs in the economy.
Individuals are unemployed due to a lack in skills that modern industries need change in technology. When mismatch occurs between availability of jobs and unemployeds skill level this is called structural unemployment. Each source of unemployment has quite different implications not only for the workers it affects but also for public policy.
This is a type of unemployment where people employed are more than actually needed. Unemployment is likely to occur at all points of the business cycle and like structural unemployment may not influence wages or inflation. Disguised unemployment is generally traced in unorganised sectors or the agricultural sectors.
Unemployment thus may be discussed broadly under several heads. There are three main types of unemployment cyclical structural and frictional unemployment. Unemployment is a hot-button issue across many of the worlds economies and many governments use unemployment rates to determine everything from economic stability to citizen satisfaction.
When individuals lose jobs due to a fall in aggregate demand often during an economic recession. When a person is employed on a day-to-day basis casual unemployment may occur due to short-term contracts shortage of raw materials fall in demand change of ownership etc. Workers may find themselves unemployed for different reasons.
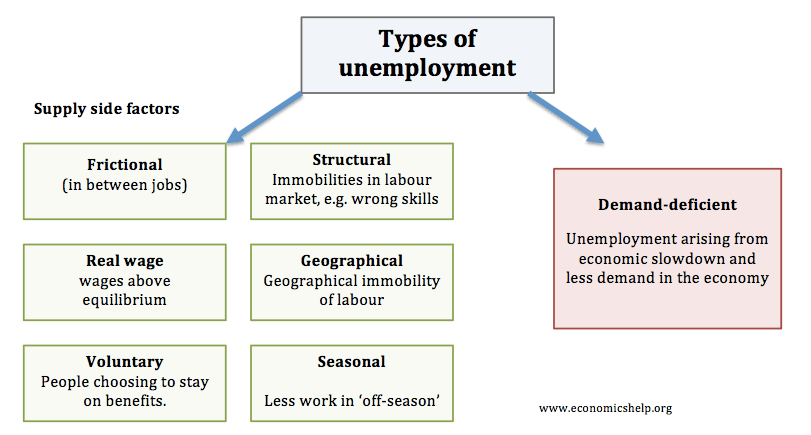
Definition Of Unemployment Economics Help

Discouraged Workers Find A Job Looking For A Job Basic Concepts
Comments
Post a Comment